Anti-Money Laundering
the challenge
Clause 5.5 of the Central Bank of Kenya (CBK) Prudential Guidelines on Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism (CBK/PG/08) requires a reporting institution to undertake a Money Laundering (ML) and Terrorism Finance (TF) risk assessment to enable it identify, assess, monitor, manage and mitigate the risks associated with money laundering and financing of terrorism.
Solution
Using Arbutus Analyzer’s workflow features, we built a risk-based weighted scoring model that assigns a numerical score on a transaction, customer, product/service or delivery channel that meet the Central Bank of Kenya behaviour markers for money laundering activities.
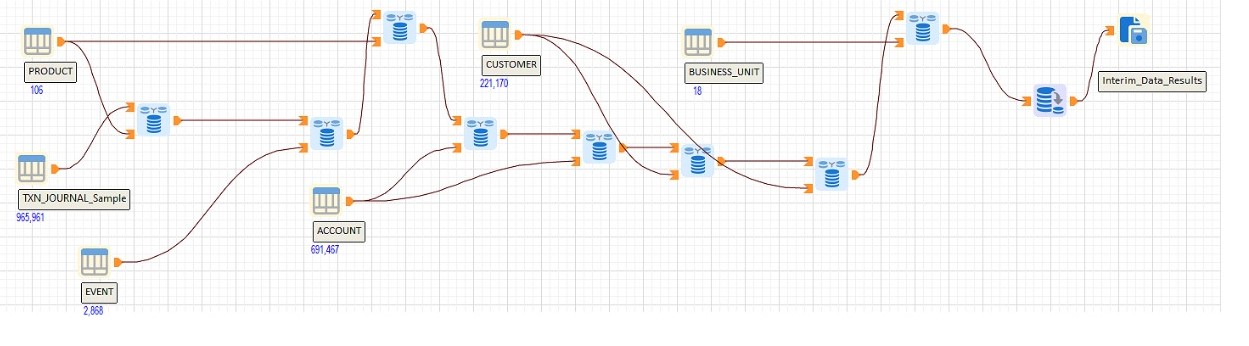
The AML (Anti-Money Laundering) detection workflow has been built using 14 unique behavioral markers that can help identify suspect transactions. Behaviour markers include : newly created bank accounts that are transacting large sums, multiple large cash deposits, customers who borrow frequently while having significant deposits, etc.
The workflow starts by creating a customer behaviour profile based on data from the core banking system that is fetched every time the model runs. The data fetched includes customer accounts, transaction journals, loans and deposits tables, products and service description tables and other relevant banking data.
The model then assigns a weighted score for each transaction or customer behaviour marker that meets the CBK indicators for possible money laundering activity. Finally, the scores are evaluated and transactions or customers flagged that meet a specified threshold.
Results
Using only Arbutus Analyzer Desktop and Hub versions, a robust, scalable and highly customizable money laundering detection model was designed and deployed in a deposit taking financial institution. The organization is now compliant with CBK prudential guidelines regarding the reporting of suspected money laundering activities.
